Bacterial Identification – BID (GMP certified):
Sequencing of the Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes, followed by comparison of the resulting sequences to ribosomal gene databases, has proven to be the most accurate method available for bacterial identification, providing the highest sensitivity and specificity. BID service support customers’ regulatory requirements including environmental monitoring, tracking and trending analysis and sterility testing.
Fungal Identification – FID (GMP certified):
Sequencing of the Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes, followed by comparison of the resulting sequences to ribosomal gene databases, has proven to be the most accurate method available for yeast and mold (fungal) identification, providing the highest sensitivity and specificity. FID service support customers’ regulatory requirements including environmental monitoring, tracking and trending analysis and sterility testing.
RAPD:
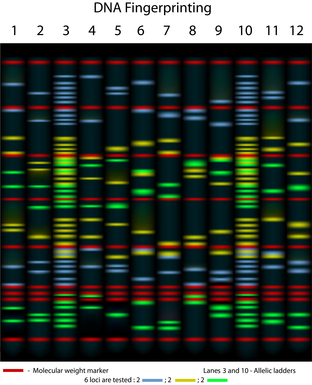
Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) is a powerful molecular method for diversity typing of bacteria and yeasts. This method consists of using a single arbitrary short primer that generates polymorphic fragments following PCR amplification and gel electrophoresis. These polymorphic fragments, used as fingerprints, allows discrimination between different strains within a species.
MLST:
Multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) is a highly discriminatory method of characterizing bacterial isolates on the basis of the sequences internal fragments of seven housekeeping genes. The data obtained by MLST can be used to address basic questions about the evolutionary and population biology of bacterial species. A major advantage of MLST is the ability to compare the results obtained in different studies via online databases.
MALDI-TOF-MS:
As a leading service lab in Israel we offer both methods – MALDI-TOF-MS and the molecular biology sequence.
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) is a powerful analytical mass spectrometry technique that is used in our lab for the identification of cultured bacteria. By identifying the unique chemical signature of each sample, bacteria can be identified down to the species level using the MALDI-TOF-MS. Samples are isolated on growth media and incubated until significant growth occurs (usually between 24-48 hours). Only when growth is observed in the isolated sample, identification procedures can take place. The MALDI-TOF-MS pulls bacterial particles mixed with ions from the matrix into a vacuum and measures each particle’s mass according to its time of flight, giving a unique signature to each sample. The information gathered is then compared to our existing database to identify the specific species of the bacteria. In case the isolate is not found in the MALDI library, it can be identified by the r-RNA sequence and that isolate can be added to the MALDI library. Also, in case the isolate is mold/fungi/yeast – molecular identification is recommended.
Ecology and Morphology:
Morphology – In addition to the identification of microorganisms we offer characterizing of microorganism’s morphology on an agar plate. This method is used to help distinguish between groups of microorganisms.
Ecology – In addition to the identification of microorganisms we offer ecology description of the identified microorganism based on known databases.
Bacterial subculture:
A subculture is a new microbiological culture made by transferring a colony of microorganism from a previous culture to fresh growth medium. A subculture is needed in order to isolate a specific microorganism from a mixture or prior to identification process.
Gram Stain test:
Although Gram stain is a very old method, it is still being used as a rapid method to release cellular products before transplantation. We are the only lab worldwide that has been approved by the FDA for that unique method. Gram stain is a differential staining technique, used for differentiation of bacteria into two groups: gram-negative and gram-positive. The differentiation is made on the basis of their cell wall structure, which serves to give the organism its size and shape as well as to prevent osmotic lysis. The material in the bacterial cell wall which confers rigidity is peptidoglycan.
- Gram-positive cell walls have a thick peptidoglycan layer beyond the plasma membrane – Gram-positive cell walls stain blue/purple with the Gram stain.
- Gram-negative cell walls are more complex, they have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane beyond the plasma membrane – Gram-negative cells will stain pink with the Gram stain.
In our lab, gram staining is used for the detecting and differentiation of bacteria from biological products produced in cell substrates, specimens and bacterial cultures.
Storing of Microbial Stock:
Creating a frozen bacterial culture for future analysis. Following Environmental monitoring, Bioburden, MLT or BID tests there is an option to prepare a stock culture of the contaminant for an analysis at a later date, stored at -80C.